At the middle course...
Middle course of river:
-gradient of slope=not as steep as upper course
-river channel wider
-other small rivers/streams may join river (tributaries)
 From the picture above, we can see that:
From the picture above, we can see that:
-river channel has become much wider and deeper
because, channel has been eroded and the river has been fed by many tributaries upstream
-surrounding valley has also become wider and flatter
-in the middle course there are many meanders (bends)
Next, these are most of the features that we saw in the middle course...
*MEANDERS
-form due to the greater volume of water carried by the river in lowland areas
-results in lateral (sideways) erosion
-causing the channel to cut into its banks forming meanders

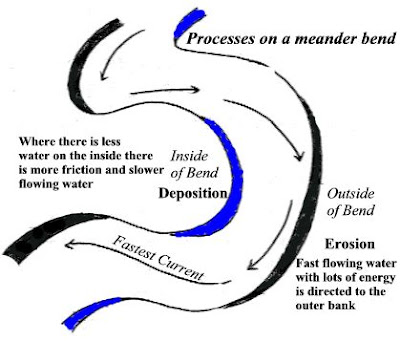
*STEEP SIDED RIVER SLOPE
-Water flows fastest on the outer bend of the river where the channel is deeper
-there is less friction
-causes greater erosion which deepens the channel
-results in the reduction in friction; increase in energy results in greater erosion -lateral erosion results in undercutting of the river bank; the formation of a steep sided river cliff.
*SLIP-OFF SLOPE
-on the inner bend water is slow flowing, due to it being a low energy
-deposition occurs resulting in a shallower channel
-thus, increases friction further; encouraging further deposition
-Over time, a small beach of material builds up on the inner bend
-this is called a slip-off slope.
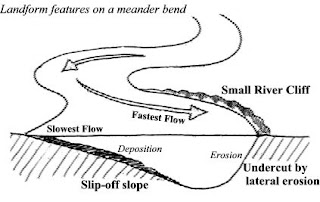
*It is deeper on the outer bend (due to greater erosion) and shallower on the inside bend (an area of deposition).*
*Ox-bow Lake Formation
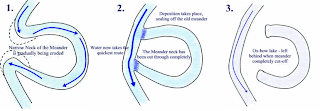
1. As the outer banks of a meander continue to be eroded through processes such as hydraulic action the neck of the meander becomes narrow and narrower.
2. Eventually, the two outer bends meet and the river cuts through the neck of the meander. The water now takes its shortest route rather than flowing around the bend.
3. Deposition gradually seals off the old meander bend forming a new straighter river channel.
4. Due to deposition the old meander bend is left isolated from the main channel as an ox-bow lake.
5. Over time this feature may fill up with sediment and may gradually dry up (except for periods of heavy rain). When the water dries up, the feature left behind is known as a meander scar.
A Video on the formation of the ox-bow lakes:

**http://www.cleo.net.uk/resources/displayframe.php?src=309/consultants_resources%2F_files%2Fmeander4.swf
A summary on what we actually saw:
1.)Meander - a bend in a river
2.)River Cliff - a small cliff formed on the outside of a meander bend due to erosion in this high energy zone.
3.)Slip off Slope - a small beach found on the inside of a meander bend where deposition has occured in the low energy zone.
4.)Ox-bow lake - a lake formed when the continued narrowing of a meander neck results in the eventual cut through of the neck as two outer bends join. This result in the straightening of the river channel and the old meander bend becomes cut off forming an ox-bow lake.
5.)Meander scar - feature left behind when the water in an ox-bow lake dries up.
-gradient of slope=not as steep as upper course
-river channel wider
-other small rivers/streams may join river (tributaries)
 From the picture above, we can see that:
From the picture above, we can see that:
-river channel has become much wider and deeper
because, channel has been eroded and the river has been fed by many tributaries upstream
-surrounding valley has also become wider and flatter
-in the middle course there are many meanders (bends)
Next, these are most of the features that we saw in the middle course...
*MEANDERS
-form due to the greater volume of water carried by the river in lowland areas
-results in lateral (sideways) erosion
-causing the channel to cut into its banks forming meanders


*STEEP SIDED RIVER SLOPE
-Water flows fastest on the outer bend of the river where the channel is deeper
-there is less friction
-causes greater erosion which deepens the channel
-results in the reduction in friction; increase in energy results in greater erosion -lateral erosion results in undercutting of the river bank; the formation of a steep sided river cliff.
*SLIP-OFF SLOPE
-on the inner bend water is slow flowing, due to it being a low energy
-deposition occurs resulting in a shallower channel
-thus, increases friction further; encouraging further deposition
-Over time, a small beach of material builds up on the inner bend
-this is called a slip-off slope.

*It is deeper on the outer bend (due to greater erosion) and shallower on the inside bend (an area of deposition).*
*Ox-bow Lake Formation

1. As the outer banks of a meander continue to be eroded through processes such as hydraulic action the neck of the meander becomes narrow and narrower.
2. Eventually, the two outer bends meet and the river cuts through the neck of the meander. The water now takes its shortest route rather than flowing around the bend.
3. Deposition gradually seals off the old meander bend forming a new straighter river channel.
4. Due to deposition the old meander bend is left isolated from the main channel as an ox-bow lake.
5. Over time this feature may fill up with sediment and may gradually dry up (except for periods of heavy rain). When the water dries up, the feature left behind is known as a meander scar.
A Video on the formation of the ox-bow lakes:

**http://www.cleo.net.uk/resources/displayframe.php?src=309/consultants_resources%2F_files%2Fmeander4.swf
A summary on what we actually saw:
1.)Meander - a bend in a river
2.)River Cliff - a small cliff formed on the outside of a meander bend due to erosion in this high energy zone.
3.)Slip off Slope - a small beach found on the inside of a meander bend where deposition has occured in the low energy zone.
4.)Ox-bow lake - a lake formed when the continued narrowing of a meander neck results in the eventual cut through of the neck as two outer bends join. This result in the straightening of the river channel and the old meander bend becomes cut off forming an ox-bow lake.
5.)Meander scar - feature left behind when the water in an ox-bow lake dries up.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home