Lower Course of the River - Floodplains and Levées
This is the view of the middle course and also the upper course of the view:
Beautiful.. isn't it?
At the lower course of the river:
-gradient is gentle
-river channel is wider than middle course
-volume of water flowing increases as more tributaries joined the river
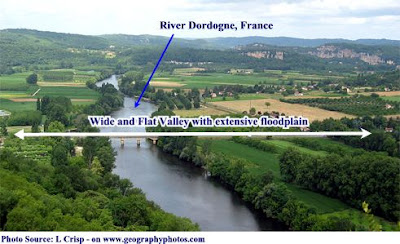
FLOODPLAIN AND LEVEES
Know what I saw? People living on the floodplains! From the term floodplains we could see that flood occurs frequently there. I learned a lesson from the villagers about how floodplains and levees are formed:
-As the river continues its journey towards the sea, the valley cross section continues to become wider and flatter with an extensive floodplain either side of the channel. -The river erodes laterally and deposition also becomes important.
-The time it reaches the lower course the river is wider and deeper and may contain a large amount of suspended sediment.
-When the river floods over the surrounding land it loses energy and deposition of its suspended load occurs.
-Regular flooding results in the building up of layers of nutrient rich alluvium which forms a flat and fertile floodplain.
Interesting right?
Here's a picture of a floodplain I took:

BRAIDED STREAM
A network of converging and diverging streams separated from each other by narrow strips of sand and gravel.
A picture of the braided stream I took

I've learnt another lesson from the villagers:
Here are the conditions of the formation of a braided stream:
* an abundant supply of sediment
* high stream gradient
* rapid and frequent variations in water discharge
* erodible banks
Nature is so amazing~!
TRIBUTARY
Where two streams (or rivers) join, the smaller one is called the tributary. The place where the two streams join is called the confluence.


Beautiful.. isn't it?
At the lower course of the river:
-gradient is gentle
-river channel is wider than middle course
-volume of water flowing increases as more tributaries joined the river
FLOODPLAIN AND LEVEES
Know what I saw? People living on the floodplains! From the term floodplains we could see that flood occurs frequently there. I learned a lesson from the villagers about how floodplains and levees are formed:
-As the river continues its journey towards the sea, the valley cross section continues to become wider and flatter with an extensive floodplain either side of the channel. -The river erodes laterally and deposition also becomes important.
-The time it reaches the lower course the river is wider and deeper and may contain a large amount of suspended sediment.
-When the river floods over the surrounding land it loses energy and deposition of its suspended load occurs.
-Regular flooding results in the building up of layers of nutrient rich alluvium which forms a flat and fertile floodplain.
Interesting right?
Here's a picture of a floodplain I took:

BRAIDED STREAM
A network of converging and diverging streams separated from each other by narrow strips of sand and gravel.
A picture of the braided stream I took

I've learnt another lesson from the villagers:
Here are the conditions of the formation of a braided stream:
* an abundant supply of sediment
* high stream gradient
* rapid and frequent variations in water discharge
* erodible banks
Nature is so amazing~!
TRIBUTARY
Where two streams (or rivers) join, the smaller one is called the tributary. The place where the two streams join is called the confluence.


0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home