At the upper course of the river, we saw...
At the upper course of the river, these are the features that were more visible and more interesting.
As the river moves through the upper course it cuts downwards. The gradient here is steep and the river channel is narrow. Vertical erosion in this highland part of the river helps to create steep sided V-shaped valleys, interlocking spurs, rapids, waterfalls and gorges:
* As the river erodes the landscape in the upper course, it winds and bends to avoid areas of hard rock. This creates interlocking spurs which look a bit like the interlocking parts of a zip.
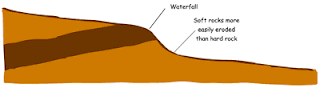
* When a river runs over alternating layers of hard and soft rock, rapids and waterfalls may form. The graphic shows how waterfalls and rapids are formed.

V-shaped Valley - a valley which resembles a 'v' in cross section. These valleys have steep sloping sides and narrow bottoms.
Interlocking Spur - spurs are ridges of more resistant rock around which a river is forced to wind as it passes downstream in the upper course. Interlocking spurs form where the river is forced to swing from side to side around these more resistant ridges.

*POTHOLES:
-formed by corrasion
-Pebbles carried by the river are swirled around on the riverbed
-erodes the rock on the riverbed forming potholes
-Over time, they may widen and join with other potholes to form larger potholes, and the whole riverbed is deepened.

*RAPIDS:
-stretches of fast-flowing water tumbling over a rocky-shallow riverbed
-Different resistance among rocks cause rapids
-formed when the water goes from one hard rock (resists the water's erosion to a softer rock that is easier eroded)

*WATERFALL
-sudden,steep of fast flowing water
-usually round in upper course of river
**Waterfalls occur when a band of hard rock lies across the river with softer rock downstream which is more rapidly eroded. At first rapids would form but then develop into a waterfall as the softer rock erodes further. Variations may be caused by the rock structure.
(1) Rock layer is horizontal
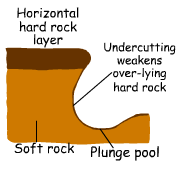
(2) Rock layer dips upstream

(3) Rock layer is vertical

*GORGES
-river flows through an area with resistant rocks by its side
-over time, deep narrow, steep sided valley: gorge
-eg, Katherin gorge
Formation:
-river flows over an area of resistant rocks
-river erodes vertically
-vertical errosion continues and a steep sided valley called gorge
that's the end of the upper course of the river. isn't that amazing?


aren't this pictures beautiful? seeing them just want me to stay here forever...
As the river moves through the upper course it cuts downwards. The gradient here is steep and the river channel is narrow. Vertical erosion in this highland part of the river helps to create steep sided V-shaped valleys, interlocking spurs, rapids, waterfalls and gorges:
* As the river erodes the landscape in the upper course, it winds and bends to avoid areas of hard rock. This creates interlocking spurs which look a bit like the interlocking parts of a zip.
* When a river runs over alternating layers of hard and soft rock, rapids and waterfalls may form. The graphic shows how waterfalls and rapids are formed.

V-shaped Valley - a valley which resembles a 'v' in cross section. These valleys have steep sloping sides and narrow bottoms.
Interlocking Spur - spurs are ridges of more resistant rock around which a river is forced to wind as it passes downstream in the upper course. Interlocking spurs form where the river is forced to swing from side to side around these more resistant ridges.

*POTHOLES:
-formed by corrasion
-Pebbles carried by the river are swirled around on the riverbed
-erodes the rock on the riverbed forming potholes
-Over time, they may widen and join with other potholes to form larger potholes, and the whole riverbed is deepened.

*RAPIDS:
-stretches of fast-flowing water tumbling over a rocky-shallow riverbed
-Different resistance among rocks cause rapids
-formed when the water goes from one hard rock (resists the water's erosion to a softer rock that is easier eroded)

*WATERFALL
-sudden,steep of fast flowing water
-usually round in upper course of river
**Waterfalls occur when a band of hard rock lies across the river with softer rock downstream which is more rapidly eroded. At first rapids would form but then develop into a waterfall as the softer rock erodes further. Variations may be caused by the rock structure.

(1) Rock layer is horizontal

(2) Rock layer dips upstream

(3) Rock layer is vertical

*GORGES
-river flows through an area with resistant rocks by its side
-over time, deep narrow, steep sided valley: gorge
-eg, Katherin gorge
Formation:
-river flows over an area of resistant rocks
-river erodes vertically
-vertical errosion continues and a steep sided valley called gorge
that's the end of the upper course of the river. isn't that amazing?


aren't this pictures beautiful? seeing them just want me to stay here forever...

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home